The Impact of
Deprivations
on Poverty
A N A L Y S I S O F H A R R I S C O U N T Y
a collaboration with Kristen Campbell, Liza Hurtubise, Kelley Reece, Kristingail Robinson, Jessica Ruland, & Edith Santamaria
Healthcare
I N D I C A T O R
HOW IT WORKS
Expenditures and out-of-pocket costs on place financial burdens on lower-income households, pushing individuals and families further into poverty because they are unable to afford preventative care.5 6
ALICE individuals and individuals living below FPL further drives a wedge between their health care needs and their health care access when if they don’t have insurance. 5
IN TEXAS…
Individuals falling in the “Texas Medicaid Coverage Gap” includes those with incomes above Medicaid eligibility level but below poverty level.7
Texas not only leads the nation in uninsured rates but is also about double the national average.7
Distribution of Those Without
Health Insurance
G E O S P A T I A L A N A L Y S I S
FIG 04 • HARRIS COUNTY POPULATION WITHOUT HEALTH INSURANCE IN 2015
(percentage of the total population by PUMA)
FIG 05 • HARRIS COUNTY POPULATION WITHOUT HEALTH INSURANCE IN 2019
(percentage of the total population by PUMA)
G E O S P A T I A L A N A L Y S I S
Distribution of Those On Public Health Insurance
FIG 06 • HARRIS COUNTY POPULATION ON PUBLIC HEALTH INSURANCE IN 2015
(percentage of the total population by PUMA)
FIG 07 • HARRIS COUNTY POPULATION ON PUBLIC HEALTH INSURANCE IN 2019
(percentage of the total population by PUMA)
I N D I C A T O R
Education
The Myth of Meritocracy
The Functionalist Theory of Industrialism holds that education (particularly higher education) is the key to preparing youth of today for the jobs of tomorrow, leading to a society run by the most talented than the most privileged. 9
The Functionalist Theory of Industrialism has given way to the neo-liberal theory that encourages 'market' instead of 'meritocratic' competition as the route to an efficient, fair and competitive economy. 9
Public Schools should be an equalizer of meritocracy and equality of opportunity.
In the modern U.S. economy, it takes five generations for someone born into poverty to earn average income levels.11
The school you are zoned to often determines your academic achievement, earning potential, and social mobility, however, due to socioeconomic and racial segregation schools do not often promote equality of opportunity. 10
HOUSTON RANKS 15TH OUT OF 250 MAJOR CITIES IN SOCIAL MOBIILITY
in 7 of 19 districts 50% of student pop. is economically disadvantaged
in 5 of 19 districts 80% of student pop. is economically disadvantaged
G E O S P A T I A L A N A L Y S I S
Population Without High School Diploma Distribution
FIG 08 • HARRIS COUNTY POPULATION WITHOUT HIGH SCHOOL DIPLOMA IN 2015
(percentage of the total population by PUMA)
FIG 09 • HARRIS COUNTY POPULATION WITHOUT HIGH SCHOOL DIPLOMA IN 2019
(percentage of the total population by PUMA)
I N D I C A T O R
Housing
hou•sing cost bur•dened
/ˈhouziNG kôst ˈbərdn/
those who spend more than 30% of their monthly income on housing costs
Research shows a link between homeownership and wealth building.Housing costs drive how occupants distribute income to meet other essential needs. 12
Research suggests that poverty measures should take living costs and housing tenure into consideration due to the impact that mortgage-free homeownership has on regional poverty rates. 13
In Harris County, 50% of renters are housing cost-burdened compared to the 20.5% of homeowners are cost-burdened. 14
G E O S P A T I A L A N A L Y S I S
Homeowner Distribution
FIG 10 • HARRIS COUNTY HOME OWNERS IN 2015
(percentage of the total population by PUMA)
FIG 11 • HARRIS COUNTY HOME OWNERS IN IN 2019
(percentage of the total population by PUMA)
I N D I C A T O R
Internet
The Digital Divide
The digital divide refers to the affordability of the technology required to access the internet, digital literacy skills, infrastructural barriers, and social barriers to internet access, particularly poverty. It is a phenomenon connected to social and economic exclusions associated with the globalized economy and neo-liberal policies.15
Those without the means to afford a home internet subscription are consequently made more economically vulnerable.
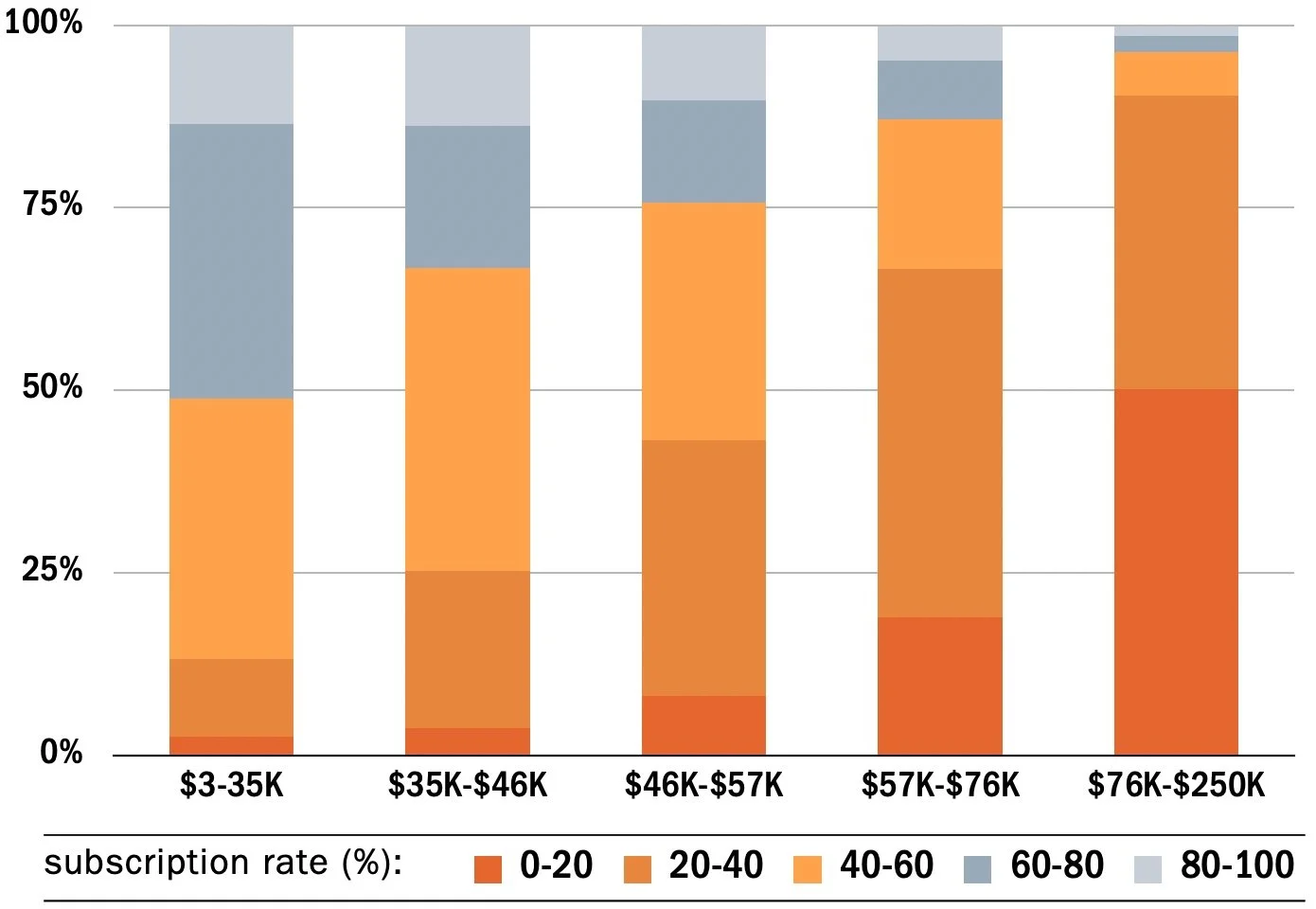
FOR NEIGHBORHOODS WITH LOW TO HIGH MEDIAN HOUSEHOLD INCOME
The Homework Divide
The homework divide is the most compelling reasons that barriers to internet access is linked to poverty. 1 in 3 low-income households in the U.S. do not have a home broadband connection, almost 70% of U.S. School teachers assign homework that requires one. 16
Researchers found that many students were prevented from completing assignments entirely while others complete assignments via cellphones through public wifi hotspots. 17
FOR NEIGHBORHOODS WITH LOW TO HIGH SHARES OF RESIDENTS WHO HAVE NOT ATTAINED EDUCATION BEYOND HIGH SCHOOL
G E O S P A T I A L A N A L Y S I S
Population Without Internet
FIG 08 • HARRIS COUNTY POPULATION WITHOUT INTERNET IN 2015
(percentage of the total population by PUMA)
FIG 09 • HARRIS COUNTY POPULATION WITHOUT INTERNET IN 2019
(percentage of the total population by PUMA)
I N D I C A T O R
Contact with the Criminal Justice System
Criminal justice system interactions can be both a cause and a consequence of poverty because…
Poorer communities are disproportionately policed. 19
Poverty prevents those convicted from meeting full conditions of their sentences. Failure to pay court fees, probation costs, and other punitive fines lead to probation violations, added charges, and further incarceration.19
Job Related Damages
In Texas, the State may suspend the drivers licenses of individuals who do not pay fines or fees associated with their cases, which in a city like Houston, damages employment opportunities. 20
Stigma associated with criminal records prevents those previously incarcerated from securing employment. 21
Those unable to pay pretrial bonds or bail remain in detention until they can raise the money or their case is adjudicated. Detention lasting longer than a few days results in job loss. 22
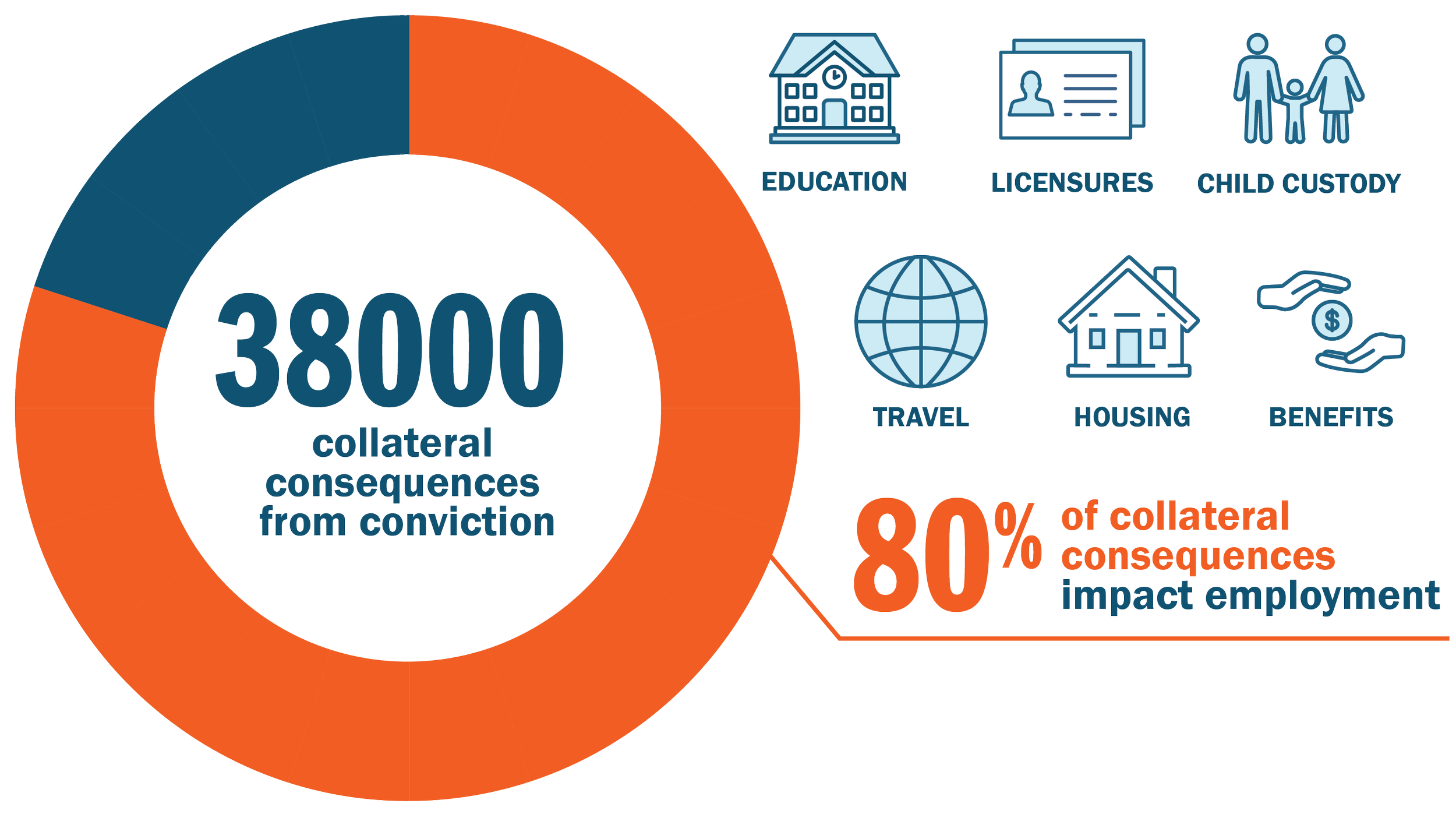
Collateral Consequences
The American Bar Association documented over 38,000 collateral consequence statutes that place a myriad of roadblocks before those convicted of criminal offenses, including barriers to housing, employment, voting, and many public benefits. Interestingly, the ABA noted that of the 38,000 statutes, 80 percent can be used to deny employment.19, 24
Distribution of Population with Court Cases
G E O S P A T I A L A N A L Y S I S
FIG 10 • HARRIS COUNTY POPULATION WITH ACTIVE COURT CASES IN 2015
(percentage of the total population by PUMA)
FIG 11 • HARRIS COUNTY POPULATION WITH ACTIVE COURT CASES IN 2019
(percentage of the total population by PUMA)